lv range | creatinine level range lv range “3.1 Low Voltage (LV): A class of nominal system voltages 1,000V or less. 3.2 Medium Voltage (MV): A class of nominal system voltages greater than 1,000V and less than 100kV. 3.3 High Voltage (HV): A class of nominal system voltages equal to or greater than 100kV and equal to or less than 230kV.
Amana Overseas Co. Inc. at 1155 Boulevard René-Lévesque O Suite 2500, Montreal, QC H3B 2K4. Get Amana Overseas Co. Inc. can be contacted at 514-819-9729. Get .
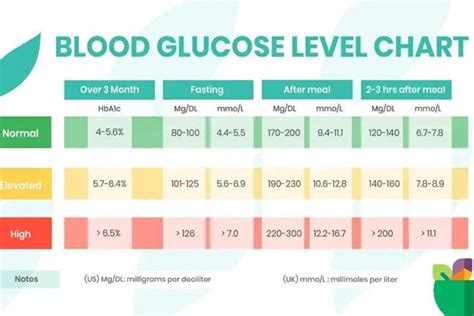
0 · random sugar level range
1 · normal range for lab tests
2 · glucose level range
3 · folate levels range
4 · creatinine level range
5 · blood glucose levels chart
6 · bilirubin level range
7 · b12 levels range
American Eagle Oversized Corduroy Jacket. American Eagle Outfitters. $40 $90. Size. XL. Buy Now. Like and save for later. Add To Bundle. From AEO Fall 2021 collection - never worn. The color is like a deep dusty rose/salmon that they don’t sell anymore. Perfect condition. Has been hanging in my closet since the day I got it.
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.In electrical power systems low voltage most commonly refers to the mains voltages as used by domestic and light industrial and commercial consumers. "Low voltage" in this context still presents a risk of electric shock, but only a minor risk of electric arcs through the air.Typically, the voltage level between the 220kV to 760 kV is called Extra High voltages. Example for 400 kV: Dehar – Panipat Line. Example for 760kV: Anpara – Unnao. Ultra-High voltage: The ultra-high voltage lines are nothing but a voltage level above 800kV is called Ultra-high voltage. Example: 1200kV Bina National MV: 4kV to 35kV.
Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.
“3.1 Low Voltage (LV): A class of nominal system voltages 1,000V or less. 3.2 Medium Voltage (MV): A class of nominal system voltages greater than 1,000V and less than 100kV. 3.3 High Voltage (HV): A class of nominal system voltages equal to or greater than 100kV and equal to or less than 230kV.
The United States has some of the most complex voltage levels for both residential and commercial applications compared to EU and IEC countries. Basic household voltage in the US is 120V/240V, whereas most IEC countries, including the UK, EU, AUS, and NZ, use a simple 230V single phase and 400-415V three-phase voltage for domestic and small . Understanding voltage classification is essential for the proper application and safety of electrical systems. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage.
Voltage levels have been defined and classified by various National and International Standards as also by certain electric power utility companies. The following are the definitions given in various National & International Standards for AC Voltages:Definitions vary somewhat but a general guide to the voltage categories are as follows: Low Voltage (LV): up to 1000V. Medium Voltage (MV): between 1000 V and 45 kV. High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above.High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.
In electrical power systems low voltage most commonly refers to the mains voltages as used by domestic and light industrial and commercial consumers. "Low voltage" in this context still presents a risk of electric shock, but only a minor risk of electric arcs through the air.Typically, the voltage level between the 220kV to 760 kV is called Extra High voltages. Example for 400 kV: Dehar – Panipat Line. Example for 760kV: Anpara – Unnao. Ultra-High voltage: The ultra-high voltage lines are nothing but a voltage level above 800kV is called Ultra-high voltage. Example: 1200kV Bina National MV: 4kV to 35kV. Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.
“3.1 Low Voltage (LV): A class of nominal system voltages 1,000V or less. 3.2 Medium Voltage (MV): A class of nominal system voltages greater than 1,000V and less than 100kV. 3.3 High Voltage (HV): A class of nominal system voltages equal to or greater than 100kV and equal to or less than 230kV.The United States has some of the most complex voltage levels for both residential and commercial applications compared to EU and IEC countries. Basic household voltage in the US is 120V/240V, whereas most IEC countries, including the UK, EU, AUS, and NZ, use a simple 230V single phase and 400-415V three-phase voltage for domestic and small .
Understanding voltage classification is essential for the proper application and safety of electrical systems. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage.
Voltage levels have been defined and classified by various National and International Standards as also by certain electric power utility companies. The following are the definitions given in various National & International Standards for AC Voltages:
ysl muse two mini size
random sugar level range
ysl cabas chyc mini purseforum
lou mini ysl grain de poudre camera
ysl mini bag gaby
ysl showroom set
$15.29
lv range|creatinine level range